Ions and Ionic bonds (IGCSE)
Ions and ionic bonds
Core
• Describe the formation of ions by electron loss or gain
Ions are charged particles formed when atoms lose or gain electrons to achieve stable electronic configuration.
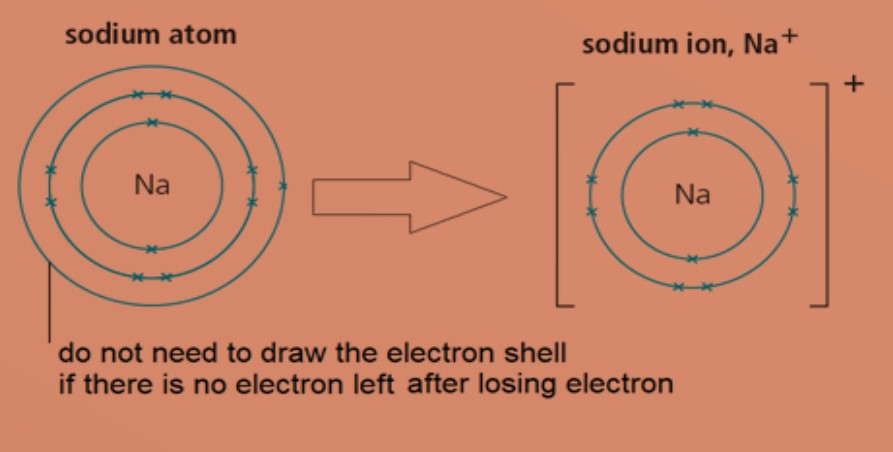
Metal atoms lose electrons to form positively charged ions (cations) .
Eg: A sodium atom has electronic configuration of 2.8.1. To obtain a stable electronic configuration of 2.8, it loses one valence electron to another atom. It becomes a sodium ion with a charge of +1.
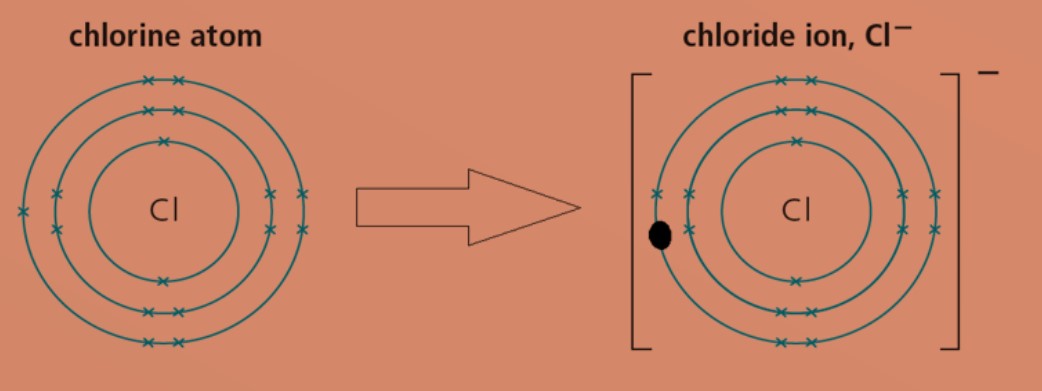
Non-metal atoms gain electrons to form negatively charged ions (anions).
Eg: A chlorine atom has electronic configuration of 2.8.7. To obtain a stable electronic configuration of 2.8.8, it gains one valence electron from another atom. It becomes a chloride ion with a charge of -1.
Examples:
| Atom |
Ion formed |
Chemical formula of ion |
| Magnesium |
Magnesium ion |
Mg2+ |
| Oxygen |
Oxide ion |
O2- |
| Aluminium |
Aluminium ion |
Al3+ |
• Describe the formation of ionic bonds between elements from Groups I and VII.
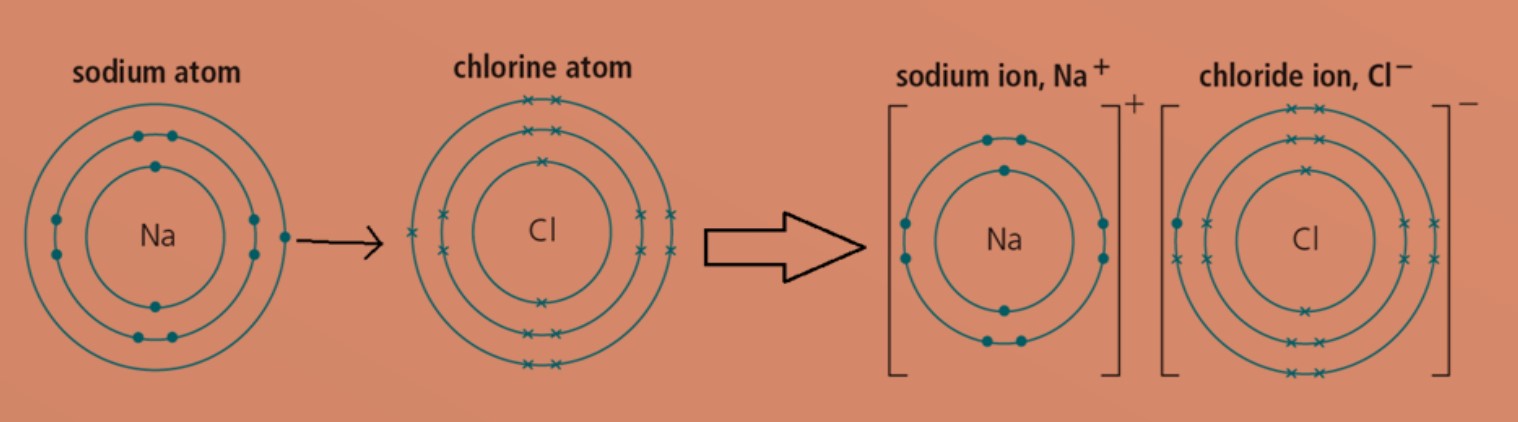
Ionic compounds are formed between metallic and non-metallic elements when they react with each other.
Eg: Sodium atom will transfer one valence electron to chlorine atom. This will form positively charged sodium ion and negatively charged chloride ion. Both ions will then achieve stable electronic configuration.
Supplement
•Describe the formation of ionic bonds between metallic and non-metallic elements.
Atoms of metallic elements will transfer electrons to atoms of non-metallic elements to achieve stable electronic configuration. This will results in electrostatic forces of attaction formed between postively and negatively charged ions.
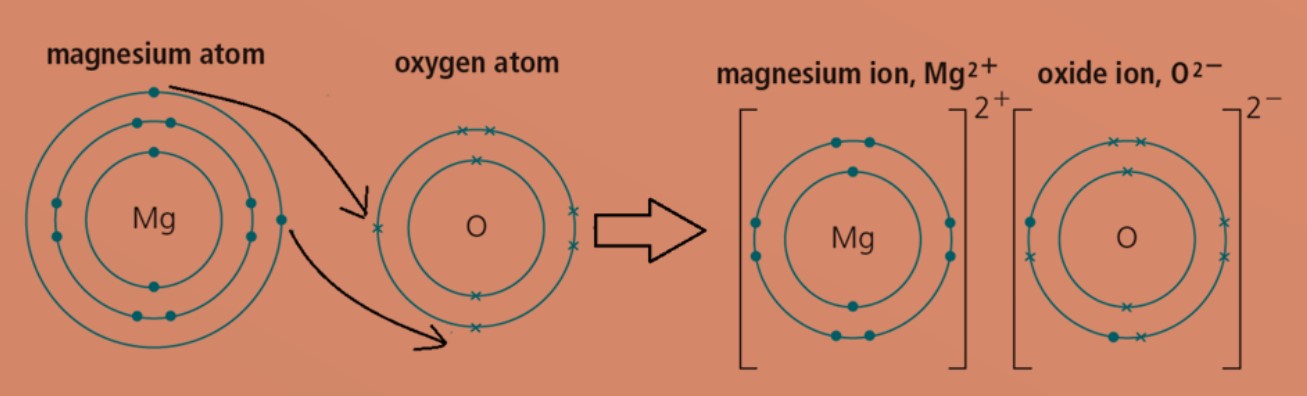
Eg 1: Magnesium oxide
magnesium atom with electronic configuration of 2.8.2 will transfer 2 valence electrons to oxygen atom with electronic configuration of 2.6. This will form positively charged magnesium ion and negatively charged oxide ion. Both ions will then achieve stable electronic configuration of 2.8. Formula of magnesium oxide is MgO.
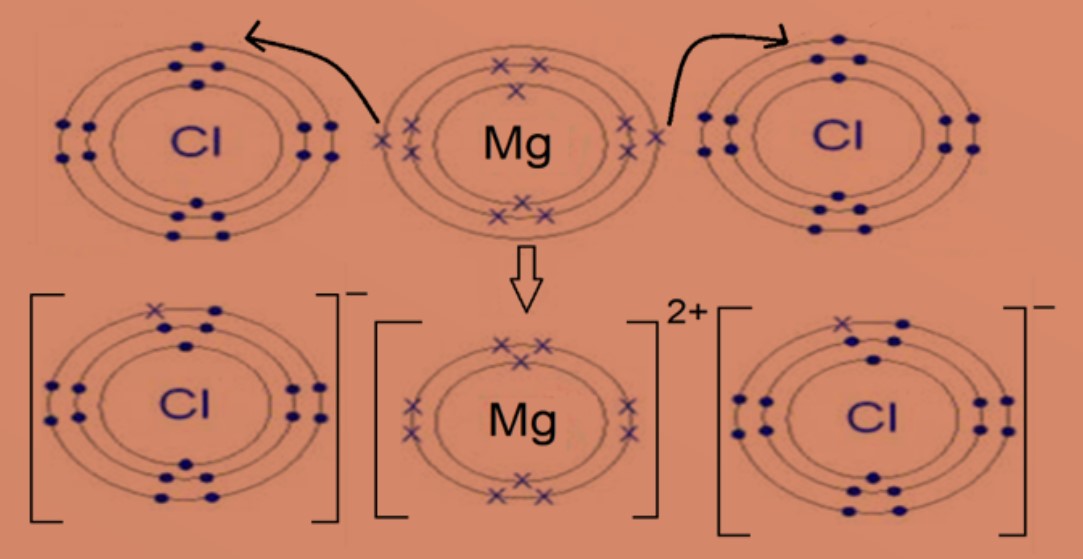
Eg 2 : Magnesium chloride
Magnesium atom with electronic configuration of 2.8.2 will transfer 2 valence electrons to two chlorine atoms. Each chlorine atom with electronic configuration of 2.6 will gain one electron. This will form positively charged magnesium ion and negatively charged chloride ion. Both ions will then achieve stable electronic configuration of 2.8. Formula of magnesium chloride is MgCl2
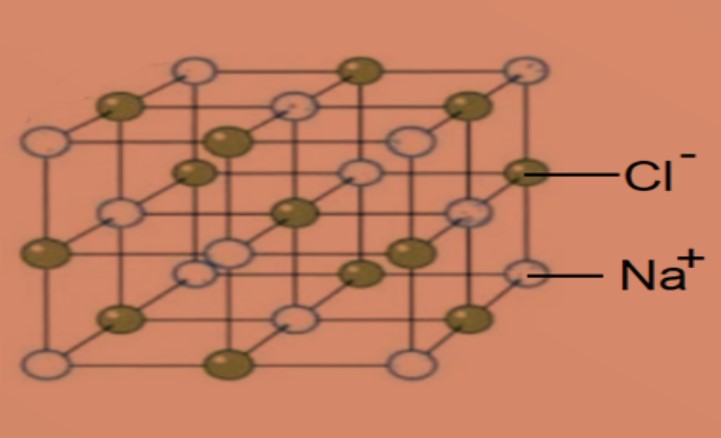
•Describe the lattice structure of ionic compounds as a regular arrangement of alternating positive and negative ions.
Oppositely charged ions form a regular pattern or lattice of alternating positive and negative ions held by strong electrostatic forces of attraction (ionic bonds).
Example of lattice structure of sodium chloride